Have you ever seen that, whenever you open a chat message on WhatsApp, there is a short message that says – “Messages and Calls are end-to-end encrypted.” Do you ever wonder what that means and how it happens? In this article, we will discuss what technology, drives and protects our privacy, and ensures the confidentiality of our data.
Nowadays, the Tech world is flourishing and with that, is the data that is being transferred, stored, and exchanged on the internet. Privacy has become quite a critical aspect but is now scarce to implement. However, there are some techniques that can be enforced to ensure that private and secured communication is established in the network.
One of those significant techniques is called the art of Cryptography. We will discuss the definition and understand the basics of the field in this column. Consequently, we will take a peek at the various uses of this technology in real-life scenarios.

What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is a method of safeguarding information and communications by encoding it in a way that only the people who need to know can interpret and process it. As a result, unwanted access to information is prevented. If we go by the literal meanings of the term – the prefix “crypt” signifies “hidden” and suffix “graphy” implies “writing”.
The procedures used to safeguard information in cryptography are derived from mathematical principles and a set of rule-based computations known as algorithms that change signals in ways that make them difficult to decipher. These algorithms are used to generate cryptographic keys, digitally sign documents, verify data privacy, browse the internet, and secure sensitive transactions like credit and card payments.
In another sense, it helps to share concealed messages that are presented in articulated boxes which can only be opened and read by a specific person who knows and has the key to open them. Now that we have a fundamental understanding of what cryptography is, let us discuss its different techniques of implementation.

History of Cryptography and its Techniques:
This method was not invented recently but dates back to the era of ancient Egyptians. Cryptography is said to have begun around 2000 B.C., with the ancient Egyptian technique of hieroglyphics. These were complicated pictograms whose entire meaning was only known by a select few.
Julius Caesar (100 B.C. to 44 B.C.) was the first known user of a modern cipher, as he did not trust his couriers while dealing with his governors and commanders. As a result, he devised a technique in which each character in his communications was substituted with a character in the Roman alphabet three positions ahead of it.
In today’s computer era, cryptography is typically connected with the process of converting plaintext to ciphertext, which is text encrypted in such a way that only the intended recipient of the information can decode it, a process known as Encryption. Decryption refers to the process of converting encrypted text to plain text.
Cryptographers are professionals who work in this sector. Their primary task is to encrypt and decrypt the messages sent via cryptography.
Important Objectives of Cryptography –
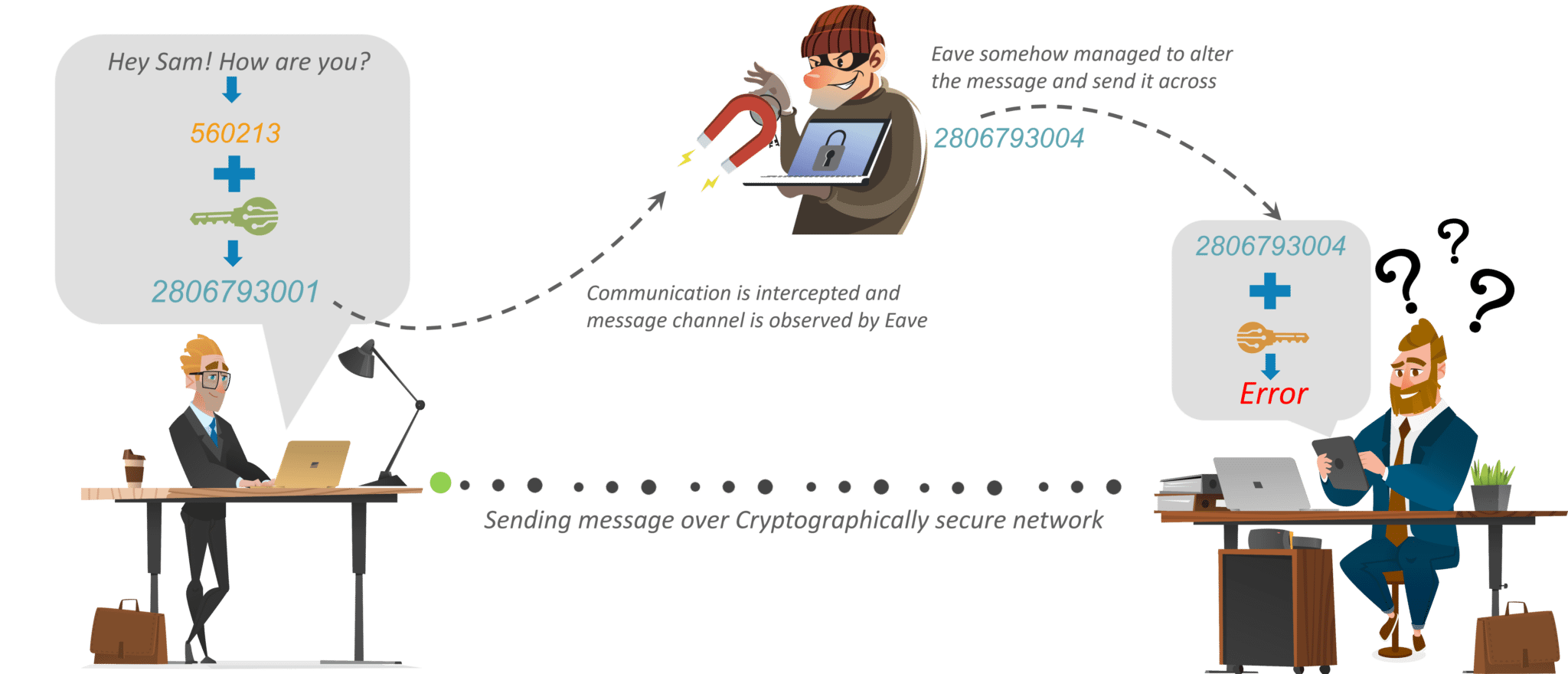
Confidentiality: Information can only be viewed by the individual for whom it is meant, and no one else can see it.
Integrity: Information cannot be changed in storage or in transit between the sender and the intended receiver without being noticed.
Non-repudiation: The creator/sender of information cannot deny that he or she intends to communicate information at a later time.
Authentication: The sender’s and receiver’s identities have been verified. The information’s destination/origin is also confirmed.
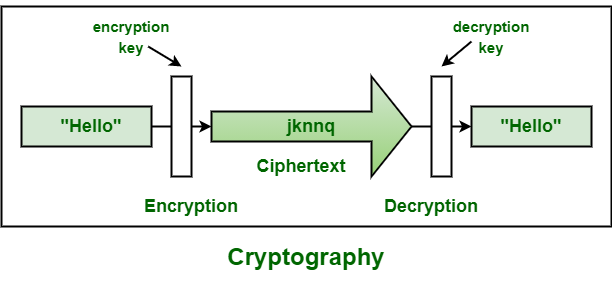
Types of Cryptography
- Symmetric Key Cryptography: It is an encryption scheme in which the sender and recipient of a message encrypt and decode messages using a single shared key. Symmetric Key Protocols are quicker and easier to use, but they have the drawback of requiring the sender and receiver to exchange keys in a safe way. Data Encryption Technology is the most widely used symmetric key encryption system (DES).
- Hash Functions: This algorithm does not make use of any keys. A hash function with a defined length is computed based on the plain text, making it difficult to reconstruct the plain text’s contents. Hash functions are used by several operating systems to encrypt passwords.
- Asymmetric Key Cryptography: This system encrypts and decrypts the information using a pair of keys. Encryption is done using a public key, while decryption is done with a private key. The terms “public key” and “private key” are not interchangeable. Even though everyone knows the public key, the intended recipient can only decrypt it since he is the only one who knows the encryption key.
Applications of Cryptography in various fields
The most vivid applications can be seen in the fields of Cybersecurity. By encrypting communications, cryptography may be used to safeguard them. HTTPS is used to encrypt websites. “End-to-end” encryption, in which only the sender and recipient can read messages, is used in Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) for email, Signal and WhatsApp for secure communications in general.
Encryption is used by operating systems to keep passwords safe, hide sections of the platform, and verify that software upgrades are genuine from the manufacturer. Instead of saving plaintext passwords, computer systems maintain hashes; when a user logs in, the system applies a cryptographic hash function to the provided credential and compares the result to the hashed value on file. The plaintext password is never accessible to the machine or an intruder in this way.
Encryption may also be used to encrypt an entire hard disk. For instance, University College London has adopted BitLocker (a Microsoft technology) to make disc contents inaccessible without requiring users to check-in.
Summing Up
Cryptography has recently become a battleground for some of the world’s most talented mathematicians and computer scientists. In both combat and business, the capacity to securely store and communicate sensitive information has proven to be crucial.
It is the modern art of security and privacy in the world of constant internet communications. It is the language of encryption and data protection. Without that, there would be havoc around the globe with all the confidentiality exposed and all the critical information left loose.
Hence, one must understand the significance of this skill and use it to make the world a better place!
Written by – Vedang Ranmale (SE ETRX)
